In today's digital-first world, businesses need more than just a simple website; they need a dynamic, interactive tool that can solve problems, streamline operations, and engage customers. That's where web application development comes in. It's a specialized field of software engineering focused on creating applications that run on remote servers and are accessed by users through a web browser. Unlike static websites that primarily display information, a web application is interactive, allowing users to manipulate data and perform tasks, much like a desktop or mobile app.
Think of the difference between a static brochure and an online banking portal. The brochure gives you information, but the banking portal lets you perform actions like checking your balance, transferring funds, and paying bills. This dynamic functionality is the core of a web app. It's what powers everything from e-commerce stores and social media platforms to project management tools and online learning platforms.
The Essential Components of a Web App
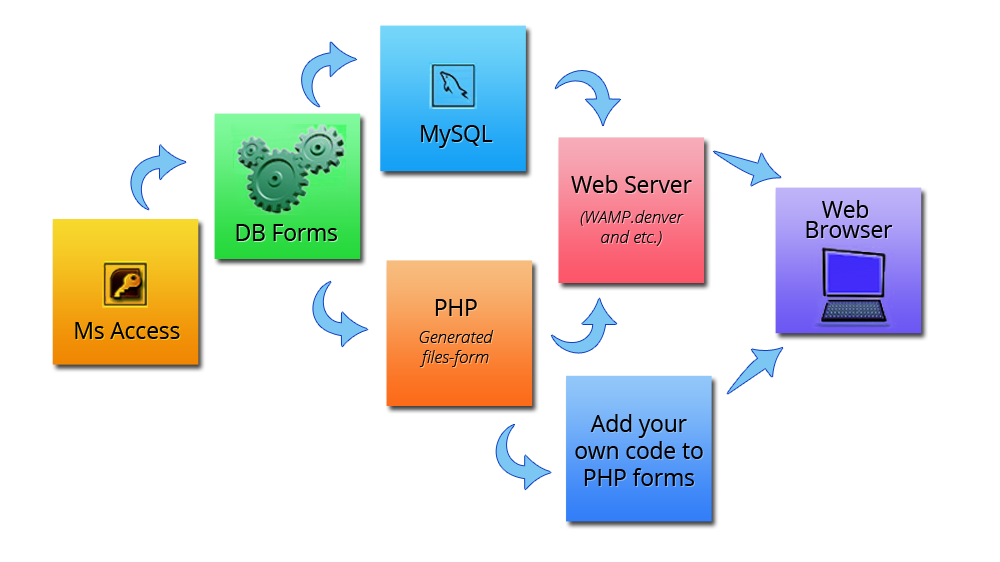
Every web application is built on a client-server architecture. This means there are two main parts:
-
Front-end (Client-side): This is the part of the app that users interact with directly. It's built using languages like HTML (the structure), CSS (the style), and JavaScript (the interactive behavior). The front-end developer's job is to create a seamless and intuitive user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) that works across different browsers and devices.
-
Back-end (Server-side): This is the "brain" of the application, handling all the logic, data storage, and processing. When you submit a form or click a button on the front-end, the request is sent to the back-end, which processes it, interacts with a database, and sends back the necessary data. Common back-end technologies include programming languages like Python, Java, PHP, and Node.js, along with frameworks like Django and Ruby on Rails.
The front-end and back-end work together to create a full-stack application. Developers who specialize in both are known as full-stack developers.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Web App Development
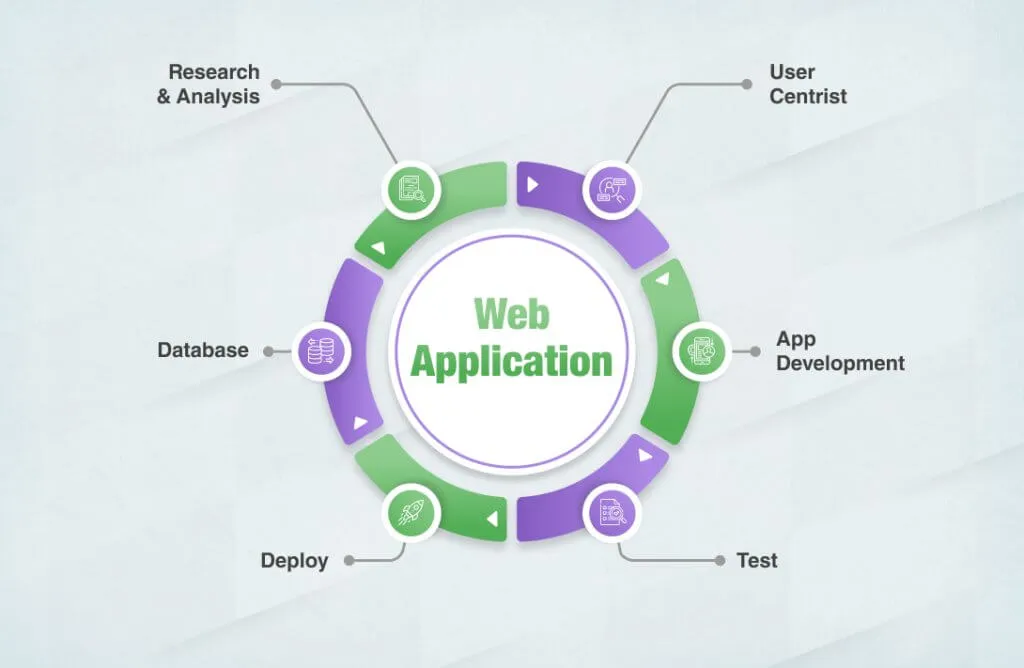
Developing a web application is a systematic process that typically follows these key stages:
-
Discovery & Planning: This is where you define the problem your app will solve. You'll outline the core features, identify your target audience, and create a roadmap for development. This stage involves market research, competitor analysis, and creating user personas.
-
Wireframing & Prototyping: Before writing a single line of code, you'll create a visual blueprint of your app. A wireframe is a low-fidelity layout, while a prototype is an interactive mockup that simulates the user flow. This helps you validate your design and get feedback early.
-
Front-end & Back-end Development: This is the core coding phase. Front-end developers build the user-facing part, while back-end developers create the server-side logic and database. This is often done simultaneously and iteratively.
-
Testing & Quality Assurance (QA): The app is rigorously tested for bugs, usability, and performance. This includes everything from checking for broken links and security vulnerabilities to ensuring the app works on different devices and browsers.
-
Deployment & Launch: Once the app is ready, it's deployed to a server where it can be accessed by the public. This involves setting up the server environment, configuring the database, and ensuring everything is running smoothly.
-
Maintenance & Updates: The journey doesn't end at launch. A successful web app requires continuous maintenance, security updates, and new features based on user feedback and changing market needs. This is a crucial, ongoing process.
Conclusion: Why Web Apps are the Future ?
Web application development is more than just a technical process; it's a strategic investment in the future of a business. Web apps offer unmatched flexibility, cross-platform compatibility, and cost-effectiveness compared to native apps. They enable businesses to reach a wider audience, streamline operations, and provide a seamless, interactive experience for their users. As technology continues to evolve, from AI integration to serverless architecture, the importance of a well-designed and robust web application will only grow.